What is insulin?
Insulin is an endogenous hormone (hormone produced by the body) that regulates the levels of glucose in the blood. It is produced by the pancreas.
What is the role of insulin?
Primarily, exogenous insulin is given to control the level of glucose in your blood. However, that is not the only role that insulin plays in your body.
Insulin is known to help regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates, protein, and fats. It is also known to aid in the formation of various bodybuilding substances.
Insulin has three main target organs in the body. These three targets are the liver, skeletal muscles, and adipose tissues.
Within the liver, insulin stimulates the conversion of glucose to its storage form (glycogen) to be used at a later time. By so doing, it decreases the level of glucose (sugar) within the blood.
It is also able to stimulate the production of fatty acids from the excess glucose in the blood.
In the skeletal muscles, insulin enhances the synthesis of proteins and glycogen from glucose.
Additionally, insulin increases the permeability of body cell membranes to some ions.
Who Should Take Insulin?
Insulin injections are usually recommended for people with diabetes. This should however be prescribed by an appropriate healthcare professional.
There are different types of insulin products available on the market and as each patient’s requirement is different, it is important to get diagnosed by an appropriate well-trained healthcare professional and the right insulin product prescribed for you according to your symptoms.
Some specific factors that can be considered when prescribing a particular kind of insulin include; age, blood sugar control, regular diet composition, weight, etc.
You may have to regularly check your blood sugar level if you are put on insulin. Reporting the recordings to your doctor or pharmacist will help them optimize your insulin dosage.
Insulin can be prescribed for other conditions like hyperkalemia. However, it is given with 50% Glucose as a short course in such a condition.
Most people who are put on insulin therapy especially in diabetes may be on it for life. Talk to your healthcare practitioner to find out whether you are going to take it for life or you would have to stop after a while.
How should insulin be taken?
Insulin can be given via:
- Subcutaneous route (Sc)
- Intramuscular route (IM)
- Intravenous route (IV)
It is usually given by the subcutaneous route. This is preferred to IM injections because the release is more prolonged and provides a sustained effect. Another reason why this route is commonly used is that it is associated with less pain.
The intravenous route is employed in emergency cases (Diabetic Ketoacidosis or Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states)
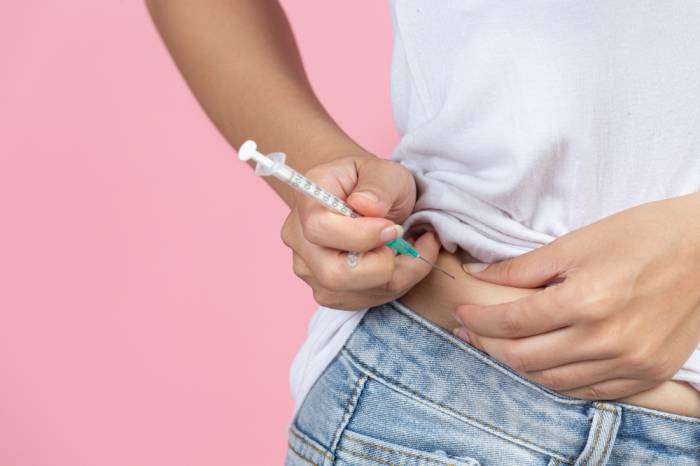
For the subcutaneous injection of insulin, it can be done in the thighs, upper arms, buttocks, or abdomen using the special insulin syringe.
You have to grasp a slight fold of the skin with your fingers at least 3 inches apart and the needle inserted at 90 degrees.
When should insulin injection be taken?
You may be asked to inject insulin once, twice or multiple times a day. That is a dose in the morning and/or at supper. This is usually dependent on the type of insulin you are using.
Insulins have been categorized based on their onset time and duration. The categories are
- Short-acting insulins
- Intermediate-acting insulins
- Long-Acting insulins
- Pre-mixed (could be a mixture of short-acting and long-acting or short-acting and intermediate-acting)
Your healthcare provider will decide which type to take and that also dictate whether to take it once or multiple times in a day.
Once you are put on an insulin regimen, you have to use it every single day until your doctor tells you otherwise.
It is not a good practice to wait until your blood sugar level is too high before injecting the insulin.
Will I continue taking the same dose of insulin every time?
The amount of insulin prescribed for you is dependent on how high your blood sugar level is. Subsequent doses will be based on how well the previous doses given were able to control your blood sugar level.
This means that your doctor can decide to increase the dose of your insulin if the previous one is not controlling your blood sugar level. In the same way, if your blood sugar level is going too low (ie. hypoglycemia), your doctor can decide to decrease your dose of insulin.
It is therefore imperative to know that your dose of insulin will not remain the same forever. You have to go for regular check-ups so that the dose that will achieve optimum blood sugar control will be prescribed at any point in time.
What will happen if a diabetic injects more insulin than necessary?
Injecting more insulin than required is known as insulin overdose and this can result in hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia means low blood sugar levels. When there is too much insulin in the body, it takes up a lot of glucose even more than necessary into the body cells and tissues. This leaves a very small concentration of glucose in the blood.
This condition (hypoglycemia) can be fatal depending on the amount of insulin that was injected and how well your body’s regulatory mechanisms work.
Some of the signs of insulin overdose or hypoglycemia include;
- Anxiety
- Sweating
- Tremors
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Increased heartbeat (Palpitations)

What should I do if I feel any of the signs/symptoms of hypoglycemia?
If you feel any of the above symptoms after injecting insulin, then you are likely to be having a low blood glucose level.
If you have a glucometer (the machine for checking blood glucose) around, quickly check at the realization of any of these symptoms. Click here to watch the proper way of checking your blood glucose using a glucometer.
If you realize that it is low (usually a value below 3mmol/L), or if you don’t have a glucometer to check but you still feel these symptoms, then you need to take some form of glucose.
In these instances, using liquids like carbonated drinks which contain glucose is recommended.
Another alternative is to use oral glucose powder if it is available. Scoop some amount into water and drink it as quickly as possible.
You can also take any raw sugar, either by putting it directly onto your tongue or dissolving it in water before taking.
What will happen if a person with a normal blood glucose level injects insulin?
For a non-diabetic, it means that the pancreas is still producing insulin in the right concentration and the body cells are still sensitive to insulin. It also means that the counter-regulatory mechanism of the body against the actions of insulin are intact.
Hence, a small amount of insulin injected into a non-diabetic may not have an adverse effect on him/her. The insulin will obviously cause a decrease in the blood sugar level but the counter regulators like glucagon will also be activated to bring back the glucose level to normal.
Nonetheless, if the amount of insulin injected is too much, it can lead to some form of hypoglycemia which will take the body a long time to reverse. In such an instance, the person may need clinical intervention in order to survive the hypoglycemia that results.
Can I use insulin if I am pregnant?
Yes. Insulin is a hormone that the body needs in order to generate energy. Since it is produced and needed by the body itself, exogenous insulin is not contra-indicated in pregnant women.
During pregnancy, your requirement for insulin may increase dramatically especially if you have diabetes. The increase in insulin demands usually begins in the second trimester.
During these periods, when using insulin, it is recommended that you also engage in self-monitoring of blood glucose level.
What is the best way to store insulin?
The storage requirements may differ slightly for each specific product. It is therefore essential that you check the product label for any special conditions that you need to observe.
However, for general purposes, the following instructions will hold for most of the insulin products out there.
Any time you go for your insulin, you will realize that it is always cold. In order words, it is always brought out of the fridge.
You are expected to store all the untouched insulin in the fridge at a temperature range of 2°C – 8°C. It is important for you to note that this temperature will keep the insulin cold but not frozen. It is important to note that your insulin product should not be frozen.
For insulin products that have already been opened, the recommendation is to store it at about 2°C – 8°C. However, some other references make mention of the fact that most of the opened insulin can be stored safely below 30°C for a period of about 30days or less.
Can frozen insulin be used?
The question you may be asking is that; Can I thaw a frozen insulin and use it after thawing?
According to the various SmPCs and manufacturer’s precautions for storage, insulin should not be frozen nor stored in the presence of light and heat to prevent spoilage of product.
Hence to be on the safer side and to ensure that you get the best of outcomes from using your insulin, make sure you don’t freeze your insulin. If your insulin ever gets frozen, you would have to discard it for a new one.
In simple terms, keep your insulin in your refrigerator but not in the freezer.






I forgot to take insulin out of the refrigerator. What is the recommended wait time at room temperature befor i use it. I can’t find that time on the internet. I usually wait 30 minutes. I can’t find any prohobition for taking refrigerated insulin, just tat it stings when injected. No one has said that first stinging dose if insulin is less effective
Once you start to use the insulin, it is recommended to keep it at a temperature below 30 degrees Celsius so there is no need to keep it refrigerated. However, if you decide to keep it in the fridge, make sure to take it out till it reaches room temperature (about 30mins) before use.
So in summary, there’s no prohibition for taking refrigerated insulin but according to the product literature, after first use, the insulin should not be refrigerated but kept below 30 degrees and used within 28days.